1. 문제 상황
프로젝트에서 AI가 추천한 장소 데이터를 한 번에 여러 개(5~10개, 경우에 따라 수백 개) 저장해야 했습니다.
처음에는 단순히 JPA의 saveAll()을 사용하고 있었고, application.yml에 Hibernate Batch 설정도 추가해 둔 상태였습니다.
spring:
jpa:
properties:
hibernate:
jdbc:
batch_size: 20
order_inserts: true
order_updates: true
기대했던 것
saveAll()을 호출하면 Hibernate가 내부적으로 JDBC Batch를 사용해서 INSERT를 여러 개 모아 한 번에 처리해 줄 것이라고 생각했습니다.
하지만 실제로는 성능이 기대만큼 나오지 않았고,
정말 Batch가 동작하는지 확인하기 위해 테스트 코드를 작성해 보기로 했습니다.
📸JPA saveAll() 100개개 성능 테스트 로그가 나온 스크린샷
2. 현재 엔티티 구조
문제가 된 엔티티는 Course였고, PK 전략은 다음과 같이 IDENTITY였습니다.
@Entity
public class Course extends BaseEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
private String address;
private Double latitude;
private Double longitude;
// ...
}
MySQL을 사용하고 있어서, IDENTITY 전략은 내부적으로 AUTO_INCREMENT 컬럼을 사용합니다.
3. 실제 동작 확인 – saveAll() 로그 관찰
먼저 10개의 데이터를 저장하면서 어떤 SQL이 실행되는지 로그를 확인해 봤습니다.
(JUnit + @DataJpaTest 기반 테스트)
@Test
@DisplayName("소량 데이터(10개)로 JPA saveAll() 로그 분석")
void testSmallBatchForLogAnalysis() {
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(10);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("소요 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
로그 결과는 기대와 달랐습니다.
text
2025-12-04T19:52:48.984 DEBUG ... INSERT into course ... -- 1번째
2025-12-04T19:52:49.028 DEBUG ... INSERT into course ... -- 2번째
2025-12-04T19:52:49.031 DEBUG ... INSERT into course ... -- 3번째
...
2025-12-04T19:52:49.072 DEBUG ... INSERT into course ... -- 10번째
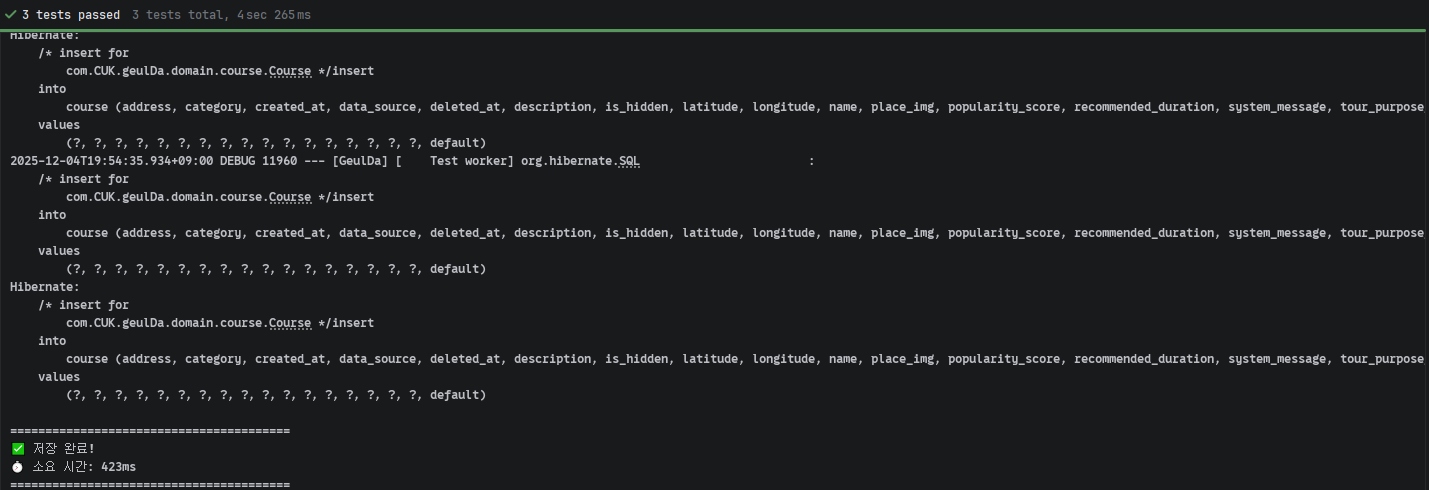
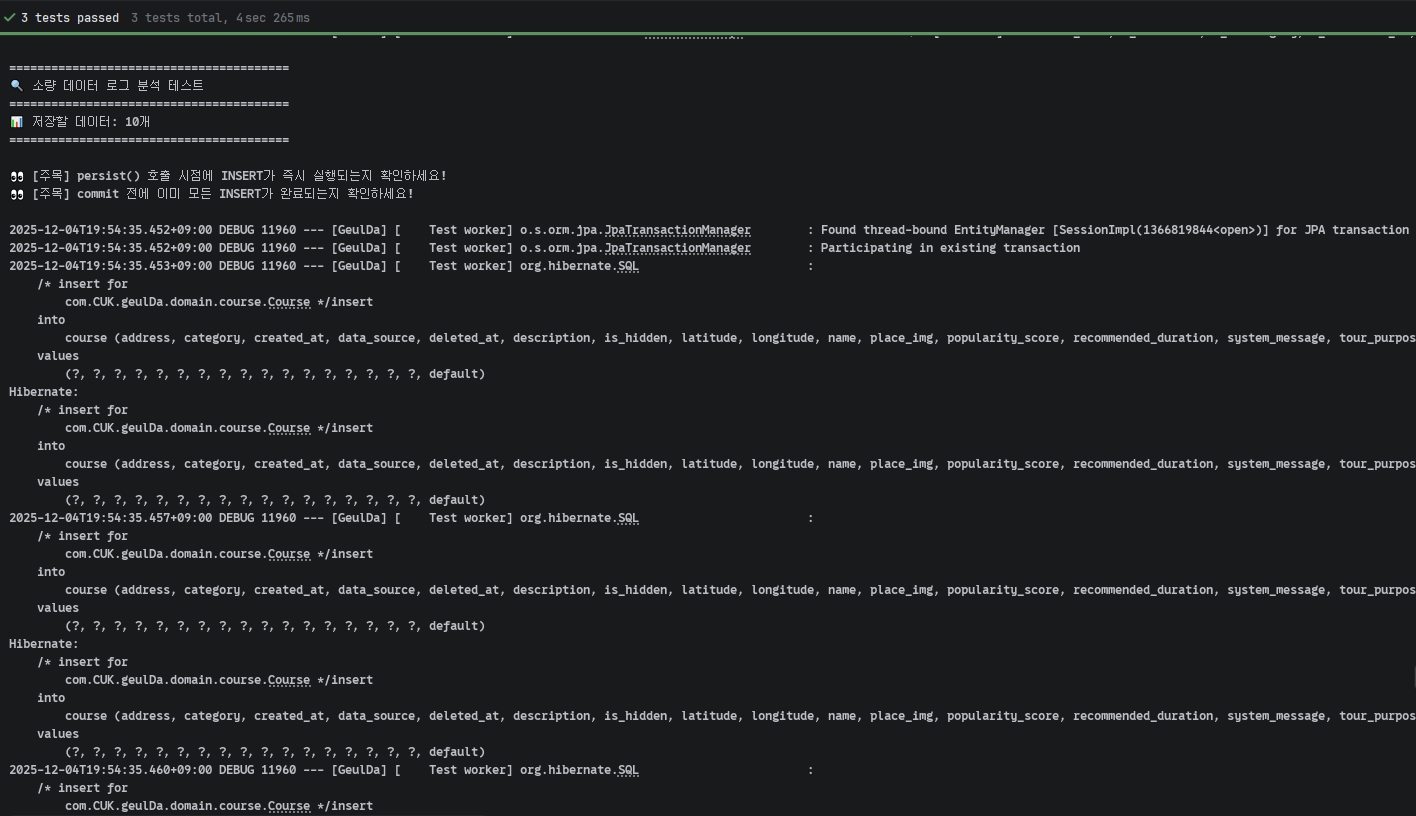
batch_size: 20으로 설정해 두었지만,10개의 INSERT 쿼리가 전부 개별적으로 실행되었습니다.saveAll()을 호출하는 시점부터 즉시 INSERT가 시작되었고, 트랜잭션commit전에 이미 모든 INSERT가 끝난 상태였습니다.
📸 10개 데이터 JPA saveAll 로그가 연속해서 찍힌 스크린샷
4. 정량적 성능 측정 – 100개, 500개
좀 더 명확한 비교를 위해 100개, 500개 데이터로 테스트를 진행했습니다.
@Test
@DisplayName("대량 데이터(500개) JPA saveAll() 성능 측정")
void testLargeBatchPerformance() {
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(500);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("총 소요 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
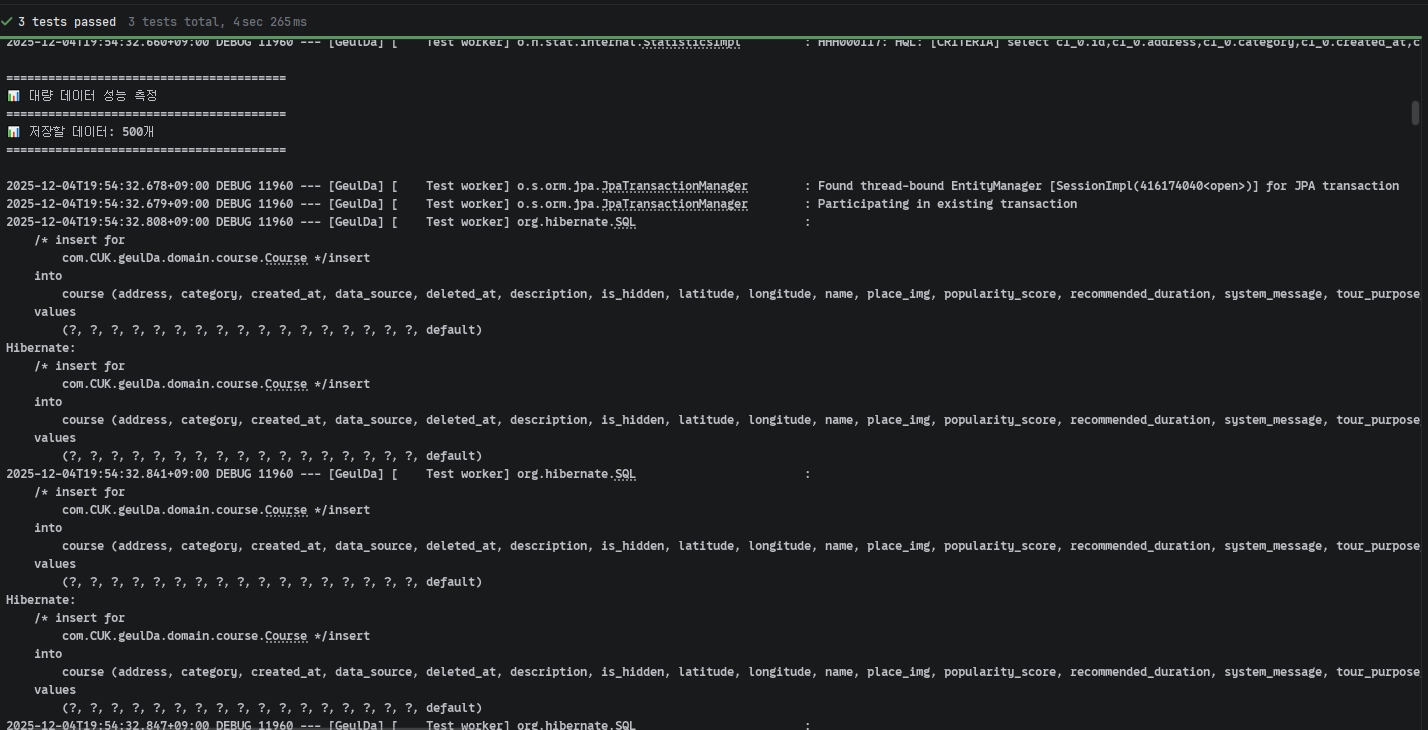
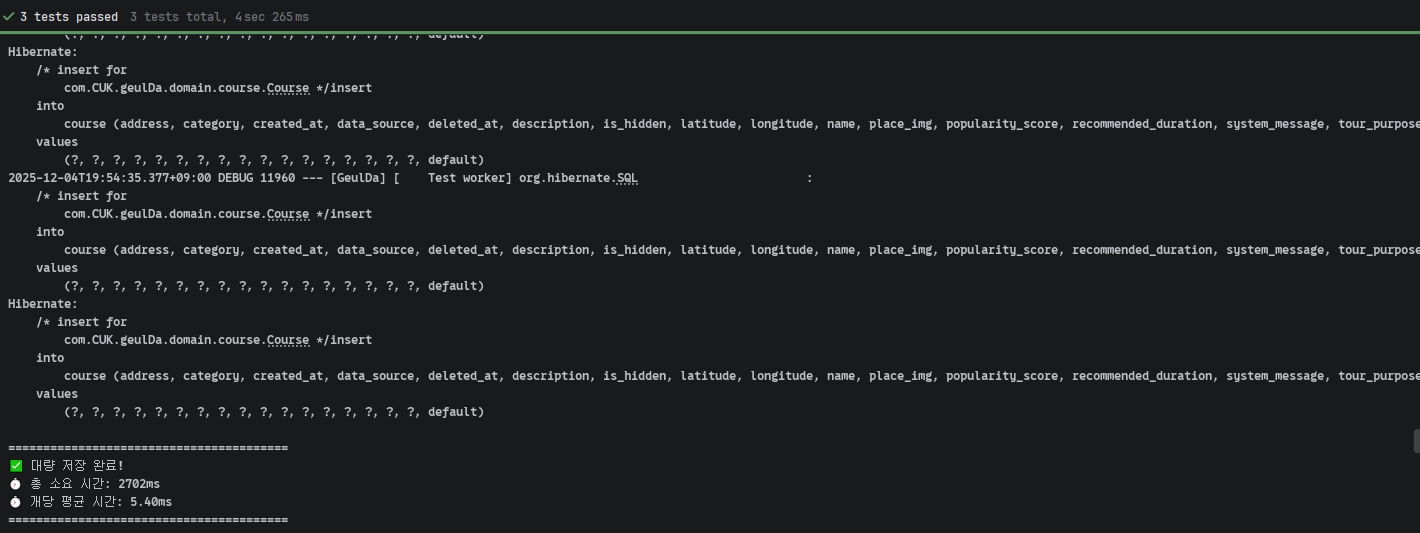
테스트 결과:
- 100개 저장: 약 423ms
- 500개 저장: 약 2702ms
📸 500개 JPA saveAll 테스트
5. 왜 Batch Insert가 동작하지 않는가? (IDENTITY 전략의 한계)
핵심은 IDENTITY 전략과 영속성 컨텍스트의 관계입니다.
- JPA 영속성 컨텍스트는 내부적으로
Map<ID, Entity>형태의 1차 캐시를 사용합니다. - 엔티티를 영속 상태로 관리하려면 반드시 ID가 있어야 합니다.
일반적으로는 이렇게 동작합니다.
SEQUENCE / TABLE 전략일 때
persist(entity)호출- DB 또는 시퀀스에서 ID를 미리 가져옴
- ID를 가진 상태로 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장
- INSERT SQL은 쓰기 지연 저장소에 모아둠
commit()시점에 한 번에 Batch로 실행 → ✅ Batch Insert 가능
IDENTITY 전략일 때
persist(entity)호출- 아직 ID 없음 (AUTO_INCREMENT는 INSERT 후에만 ID 생성)
- 영속성 컨텍스트에 넣으려면 ID가 필요 → 딜레마
- 결국 즉시 INSERT를 실행해서 ID를 받아온 뒤
- 그제서야 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장
이 흐름 때문에:
saveAll()으로 여러 개를 넣더라도각 엔티티마다 INSERT가 즉시 실행- 쓰기 지연(Write-Behind)와 JDBC Batch가 근본적으로 불가능
MySQL에서는 SEQUENCE 전략을 쓸 수 없어서,
JPA 설정만으로는 이 한계를 넘을 수 없었습니다.
6. 해결 방법: JdbcTemplate batchUpdate()로 우회
이 문제를 우회하기 위해, 영속성 컨텍스트를 아예 거치지 않는 방법을 선택했습니다.
바로 JdbcTemplate의 batchUpdate()입니다.
Batch 전용 Repository
@Repository
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CourseBatchRepository {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void batchInsert(List<Course> courses) {
String sql = """
INSERT INTO course (
name, address, description, latitude, longitude,
is_hidden, category, popularity_score, data_source,
created_at, updated_at
) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {
Course course = courses.get(i);
Timestamp now = new Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
ps.setString(1, course.getName());
ps.setString(2, course.getAddress());
ps.setString(3, course.getDescription());
ps.setDouble(4, course.getLatitude() != null ? course.getLatitude() : 0.0);
ps.setDouble(5, course.getLongitude() != null ? course.getLongitude() : 0.0);
ps.setBoolean(6, course.getIsHidden() != null ? course.getIsHidden() : false);
ps.setString(7, course.getCategory());
ps.setInt(8, course.getPopularityScore() != null ? course.getPopularityScore() : 50);
ps.setString(9, course.getDataSource() != null ? course.getDataSource() : "manual");
ps.setTimestamp(10, now);
ps.setTimestamp(11, now);
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return courses.size();
}
});
}
}
이 방식은
- JPA 영속성 컨텍스트를 완전히 우회
- 순수 JDBC 레벨에서 진짜 Batch Insert 실행
- JPA의 엔티티 매핑, 변경 감지 등의 편의 기능은 사용 불가
- 대량 INSERT가 필요한 구간에만 선택적으로 사용
7. 성능 비교 결과
같은 테스트 환경에서 JPA saveAll()과 JdbcTemplate batchUpdate()를 비교했습니다.
@Test
@DisplayName("성능 비교: JPA vs JdbcTemplate")
void testPerformanceComparison() {
List<Course> courses100 = generateTestCourses(100);
// JPA saveAll
long jpaStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses100);
long jpaEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
// JdbcTemplate batchUpdate
long jdbcStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(courses100);
long jdbcEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("JPA saveAll(): " + (jpaEnd - jpaStart) + "ms");
System.out.println("JdbcTemplate batchUpdate(): " + (jdbcEnd - jdbcStart) + "ms");
}
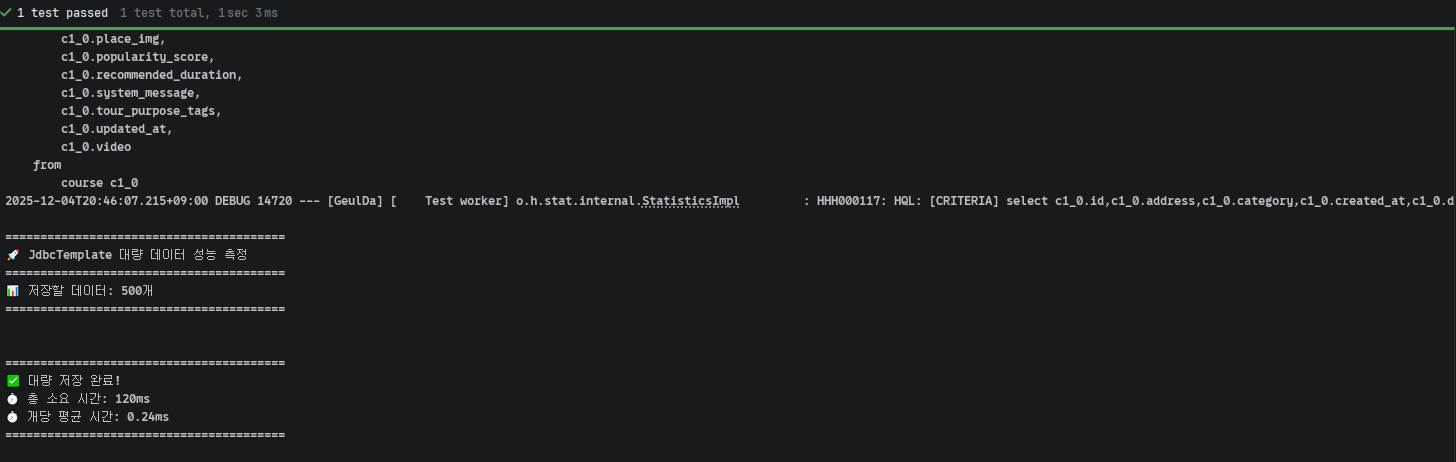
500개 데이터 저장 시
- JPA
saveAll(): 2702ms - JdbcTemplate
batchUpdate(): 120ms - 성능 향상: 95.56%
📸 JdbcTemplate 500개 테스트 결과 스크린샷
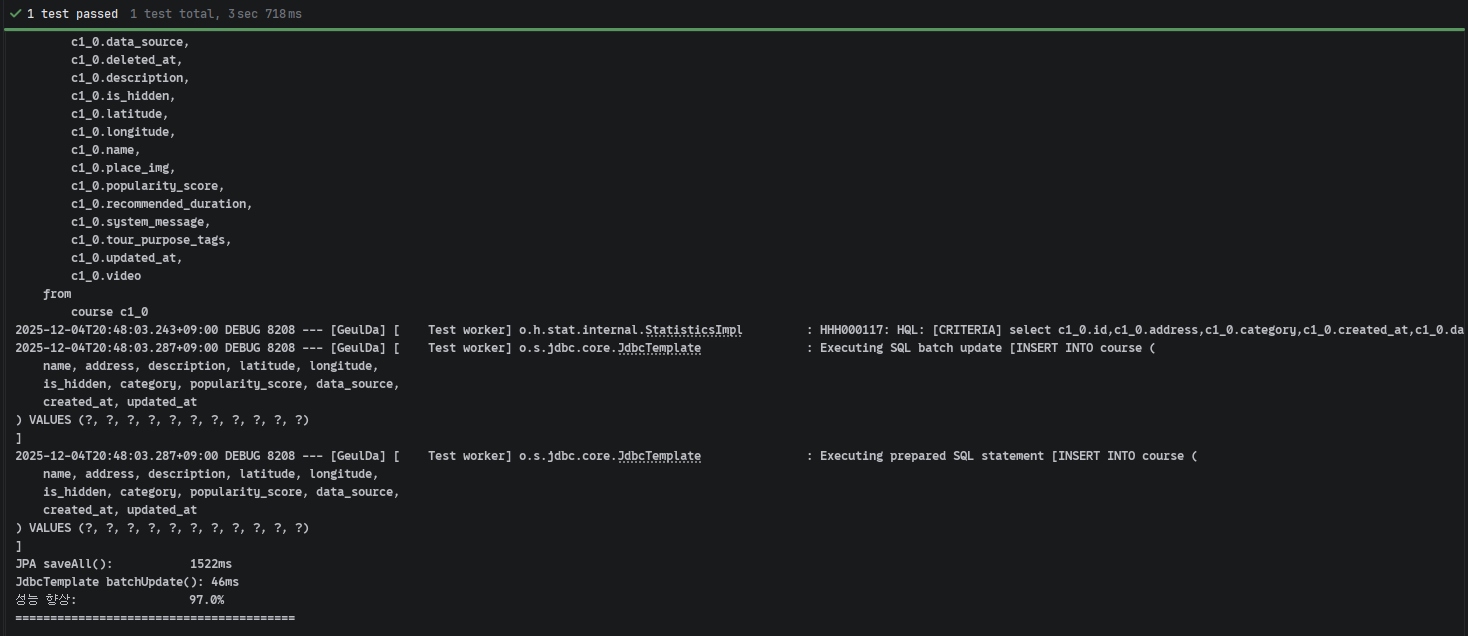
8. 최종 비교 표
| 데이터 개수 | JPA saveAll() | JdbcTemplate batchUpdate() | 개선율 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500개 | 1,522ms | 46ms | 97.0% 향상 |
📸 성능 비교 테스트 최종 결과 스크린샷
9. 실제 프로젝트 적용
프로젝트에서는 다음과 같이 하이브리드 전략을 사용했습니다.
CourseService (비즈니스 로직)
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CourseService {
private final CourseRepository courseRepository;
private final CourseBatchRepository courseBatchRepository;
@Transactional
public List<Course> saveAllCourses(List<Course> courses) {
List<Course> coursesToSave = new ArrayList<>();
List<Course> finalCourses = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 중복 검사 (JPA 사용 - 복잡한 조회 로직)
for (Course course : courses) {
List<Course> existing = courseRepository
.findByNameContainingAndIsHiddenFalse(course.getName());
boolean isDuplicate = existing.stream()
.anyMatch(e -> e.getAddress() != null &&
e.getAddress().equals(course.getAddress()));
if (isDuplicate) {
finalCourses.add(existing.get(0)); // 기존 재사용
} else {
coursesToSave.add(course); // 신규 저장 대상
}
}
// 2. 신규 데이터만 Bulk Insert (JdbcTemplate 사용)
if (!coursesToSave.isEmpty()) {
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(coursesToSave);
finalCourses.addAll(coursesToSave);
}
return finalCourses;
}
}
전략:
- 읽기 (중복 체크): JPA 사용 → 엔티티 매핑, 복잡한 쿼리 활용
- 쓰기 (대량 INSERT): JdbcTemplate 사용 → 순수 성능 최적화
10. 결론
IDENTITY 전략을 사용하는 환경에서는 Hibernate의 batch_size 설정이 동작하지 않습니다.
- 영속성 컨텍스트가 엔티티를 관리하기 위해 ID가 필수
- IDENTITY는 INSERT를 실행해야만 ID를 얻을 수 있음
- 따라서
persist()호출 즉시 INSERT 실행 → 쓰기 지연 불가능
해결책:
- SEQUENCE 전략으로 변경 (PostgreSQL, Oracle만 가능)
- JdbcTemplate
batchUpdate()사용 (MySQL 환경 권장)
실제 테스트에서 95~97%의 성능 향상을 확인했고,
500개 데이터 저장 시간이 2702ms → 120ms로 단축되었습니다.
JPA의 편의 기능을 포기해야 하는 부분이 있지만,
성능이 중요한 대량 INSERT 구간에서는 충분히 고려할 만한 선택지입니다.
11. 참고: 전체 테스트 코드
전체 테스트 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
package com.CUK.geulDa.domain.course;
import com.CUK.geulDa.domain.course.repository.CourseBatchRepository;
import com.CUK.geulDa.domain.course.repository.CourseRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.DataJpaTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* JPA IDENTITY 전략과 Batch Insert 성능 테스트
*
* 목적: IDENTITY 전략에서 Hibernate Batch 설정이 실제로 동작하는지 검증
*
* @DataJpaTest를 사용하여 JPA 관련 부분만 테스트 (독립적인 테스트)
*/
@DataJpaTest
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@Import(CourseBatchRepository.class) // JdbcTemplate 사용을 위해 수동 임포트
class CourseBatchInsertTest {
@Autowired
private CourseRepository courseRepository;
@Autowired
private CourseBatchRepository courseBatchRepository;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
courseRepository.deleteAll();
}
/**
* 테스트 데이터 생성
*/
private List<Course> generateTestCourses(int count) {
List<Course> courses = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
Course course = Course.builder()
.name("테스트 장소 " + i)
.address("서울시 강남구 테헤란로 " + i)
.description("테스트 설명 " + i)
.latitude(37.5 + (i * 0.001))
.longitude(127.0 + (i * 0.001))
.isHidden(false)
.category("카페")
.popularityScore(50)
.dataSource("test")
.build();
courses.add(course);
}
return courses;
}
@Test
@DisplayName("1단계: JPA saveAll() 성능 측정 (IDENTITY 전략)")
void testJpaSaveAll() {
// Given: 100개의 테스트 데이터
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(100);
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("🧪 JPA saveAll() 테스트 시작");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("📊 저장할 데이터: " + courses.size() + "개");
System.out.println("⚙️ Hibernate Batch 설정: batch_size=20");
System.out.println("⚙️ ID 전략: IDENTITY (AUTO_INCREMENT)");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// When: saveAll 실행 및 시간 측정
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Then: 결과 출력
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("✅ 저장 완료!");
System.out.println("⏱️ 소요 시간: " + duration + "ms");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("💡 위의 SQL 로그를 확인해보세요!");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// 검증
long savedCount = courseRepository.count();
System.out.println("📈 DB에 저장된 개수: " + savedCount + "개\n");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("2단계: 소량 데이터로 로그 자세히 관찰 (10개)")
void testSmallBatchForLogAnalysis() {
// Given: 10개의 테스트 데이터
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(10);
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("🔍 소량 데이터 로그 분석 테스트");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("📊 저장할 데이터: " + courses.size() + "개");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
System.out.println("👀 [주목] persist() 호출 시점에 INSERT가 즉시 실행되는지 확인하세요!");
System.out.println("👀 [주목] commit 전에 이미 모든 INSERT가 완료되는지 확인하세요!\n");
// When
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("\n💡 위의 로그에서 확인할 포인트:");
System.out.println("\n⏱️ 소요 시간: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms\n");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("3단계: 대량 데이터 성능 측정 (500개)")
void testLargeBatchPerformance() {
// Given: 500개의 테스트 데이터
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(500);
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("📊 대량 데이터 성능 측정");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("📊 저장할 데이터: " + courses.size() + "개");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// When
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Then
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("✅ 대량 저장 완료!");
System.out.println("⏱️ 총 소요 시간: " + duration + "ms");
System.out.println("⏱️ 개당 평균 시간: " + String.format("%.2f", duration / 500.0) + "ms");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
}
// ============================================================
// 🚀 JdbcTemplate batchUpdate() 테스트
// ============================================================
@Test
@DisplayName("4단계: JdbcTemplate batchUpdate() 100개 성능 측정")
void testJdbcBatchUpdate100() {
// Given: 100개의 테스트 데이터
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(100);
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("🚀 JdbcTemplate batchUpdate() 테스트");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("📊 저장할 데이터: " + courses.size() + "개");
System.out.println("⚙️ 방식: JdbcTemplate batchUpdate()");
System.out.println("⚙️ 영속성 컨텍스트: 우회 (직접 SQL 실행)");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// When: batchInsert 실행 및 시간 측정
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Then: 결과 출력
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("✅ 저장 완료!");
System.out.println("⏱️ 소요 시간: " + duration + "ms");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("💡 위의 SQL 로그를 확인해보세요!");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("5단계: JdbcTemplate batchUpdate() 500개 성능 측정")
void testJdbcBatchUpdate500() {
// Given: 500개의 테스트 데이터
List<Course> courses = generateTestCourses(500);
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("🚀 JdbcTemplate 대량 데이터 성능 측정");
System.out.println("========================================");
System.out.println("📊 저장할 데이터: " + courses.size() + "개");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// When
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(courses);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Then
long duration = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("✅ 대량 저장 완료!");
System.out.println("⏱️ 총 소요 시간: " + duration + "ms");
System.out.println("⏱️ 개당 평균 시간: " + String.format("%.2f", duration / 500.0) + "ms");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
}
@Test
@DisplayName("6단계: 성능 비교 테스트 (JPA vs JdbcTemplate)")
void testPerformanceComparison() {
System.out.println("\n========================================");
System.out.println("⚡ 성능 비교 테스트");
System.out.println("========================================\n");
// 테스트 1: 100개 데이터
List<Course> courses100 = generateTestCourses(100);
System.out.println("📊 [100개 데이터 비교]");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// JPA saveAll
courseRepository.deleteAll();
long jpaStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses100);
long jpaEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
long jpaDuration = jpaEnd - jpaStart;
// JdbcTemplate batchUpdate
courseRepository.deleteAll();
long jdbcStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(courses100);
long jdbcEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
long jdbcDuration = jdbcEnd - jdbcStart;
System.out.println("JPA saveAll(): " + jpaDuration + "ms");
System.out.println("JdbcTemplate batchUpdate(): " + jdbcDuration + "ms");
System.out.println("성능 향상: " + String.format("%.1f%%", (1 - (double)jdbcDuration / jpaDuration) * 100));
System.out.println("----------------------------------------\n");
// 테스트 2: 500개 데이터
List<Course> courses500 = generateTestCourses(500);
System.out.println("📊 [500개 데이터 비교]");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
// JPA saveAll
courseRepository.deleteAll();
long jpaStart500 = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseRepository.saveAll(courses500);
long jpaEnd500 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long jpaDuration500 = jpaEnd500 - jpaStart500;
// JdbcTemplate batchUpdate
courseRepository.deleteAll();
long jdbcStart500 = System.currentTimeMillis();
courseBatchRepository.batchInsert(courses500);
long jdbcEnd500 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long jdbcDuration500 = jdbcEnd500 - jdbcStart500;
System.out.println("JPA saveAll(): " + jpaDuration500 + "ms");
System.out.println("JdbcTemplate batchUpdate(): " + jdbcDuration500 + "ms");
System.out.println("성능 향상: " + String.format("%.1f%%", (1 - (double)jdbcDuration500 / jpaDuration500) * 100));
System.out.println("========================================\n");
}
}